Difference in Differences
Welcome
Introduction!
Welcome to our eighth tutorial for the Statistics II: Statistical Modeling & Causal Inference (with R) course.
During this week’s lecture you were introduced to Difference in Differences (DiD).
In this lab session we will:
- Learn how to transform our dataframes from wide to long format with
tidyr:pivot_longer() - Leverage visualizations with
ggplot2to explore changes between groups and across time - Learn how to extract our DiD estimates through manual calculation, first differences, and the regression formulation of the DiD model
1. Wide and long data formats
As we have seen throughout the semester, there are multiple ways to store our data. This week, we will look at the difference between wide and long format data.
We will illustrate this with a brief example. The two datasets we will load —city_wide_df and city_long_df— contain the same information.
Wide
# wide data frame
city_wide_df %>% knitr::kable() %>% kableExtra::kable_styling()| city | pop_2000 | pop_2010 | pop_2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Berlin | 3.38 | 3.45 | 3.56 |
| Rome | 3.70 | 3.96 | 4.26 |
| Paris | 9.74 | 10.46 | 11.01 |
| London | 7.27 | 8.04 | 9.30 |
Long
# long data frame
city_long_df %>% knitr::kable() %>% kableExtra::kable_styling()| city | year | pop |
|---|---|---|
| Berlin | 2000 | 3.38 |
| Berlin | 2010 | 3.45 |
| Berlin | 2020 | 3.56 |
| Rome | 2000 | 3.70 |
| Rome | 2010 | 3.96 |
| Rome | 2020 | 4.26 |
| Paris | 2000 | 9.74 |
| Paris | 2010 | 10.46 |
| Paris | 2020 | 11.01 |
| London | 2000 | 7.27 |
| London | 2010 | 8.04 |
| London | 2020 | 9.30 |
As we can see, the long dataset separates the unit of analysis (city-year) into two separate columns. On the other hand, the wide dataset combines one of the keys (year) with the value variable (population).
Why do we care about the data format
In some instances, long format datasets are required for advanced statistical analysis and graphing. For example, if we wanted to run the regression formulation of the difference in differences model, we would need to input our data in long format. Furthermore, having our data in long format is very useful when plotting. Packages such as ggplot2, expect that your data will be in long form for the most part.
Converting from wide to long format
We will learn how to pivot our wide format data to long format with the tidyr package.
We will use the tidyr::pivot_longer() function, which “lengthens” data, increasing the number of rows and decreasing the number of columns. The inverse transformation is tidyr::pivot_wider()
You can read the vignette here.
How to use tidyr::pivot_longer()
your_new_long_df <-
tidyr::pivot_longer(
your_wide_df,
cols,
names_to = "name",
values_to = "value"
...
)Let’s turn the city_wide_df into a long format dataset:
city_wide_df %>%
tidyr::pivot_longer(
cols = c(pop_2000, pop_2010, pop_2020), # -city, !city, dplyr::starts_with("pop_"), etc... would also work
names_to = "year", # where do we want the names of the columns to go? (year)
names_prefix = "pop_", # names_prefix removes matching text from the start of each variable name (not always necessary)
values_to = "pop" # where do we want the values in the columns to go? (pop)
)## # A tibble: 12 × 3
## city year pop
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Berlin 2000 3.38
## 2 Berlin 2010 3.45
## 3 Berlin 2020 3.56
## 4 Rome 2000 3.7
## 5 Rome 2010 3.96
## 6 Rome 2020 4.26
## 7 Paris 2000 9.74
## 8 Paris 2010 10.5
## 9 Paris 2020 11.0
## 10 London 2000 7.27
## 11 London 2010 8.04
## 12 London 2020 9.3Try to delete the names_prefix = "pop_" argument to see what happens.
Let’s move to our practical example to see how we can use R for DiD estimation.
2. Measuring the effect of a soda tax on sugar-added drink consumption
After the very successful impact evaluations you have performed in the past weeks, you are contacted by the local government of Pawnee, Indiana. The city is interested in your advice to assess a policy intervention passed with the support of councilwoman Leslie Knope.
The city of Pawnee has been at the spotlight recently, as it has come to be known as the child obesity and diabetes capital of the state of Indiana. Some of the constituents of the city point at the fast food culture and soda sizes across the restaurants in town as a source of the problem. The largest food chain in Pawnee, Paunch Burger, offers its smallest soda size at a whopping 64oz (about 1.9 liters).
The “soda tax”, as it came to be known, came to effect initially at a couple of districts. Fortunately for you, based on an archaic law, residents of Indiana have to demonstrate their residence in the district they intend to dine before being served at any of the restaurants. The latter fact means that Pawnee inhabitants can only buy sugar-added drinks in their respective home district.

Packages
# These are the libraries we will use today. Make sure to install them in your console in case you have not done so previously.
set.seed(42) #for consistent results
library(dplyr) # to wrangle our data
library(tidyr) # to wrangle our data - pivot_longer()
library(ggplot2) # to render our graphs
library(readr) # for loading the .csv data
library(kableExtra) # to render better formatted tables
library(stargazer) # for formatting your model output
library(estimatr) # to employ lm_robust()
soda_tax_df <- readr::read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/seramirezruiz/hertiestats2/master/data/soda_tax_df.csv") # simulated dataOur dataset soda_tax_df, contains the following information:
ìd: A unique number identifier for each of the 7,500 inhabitants of Pawneedistrict: The name of the district in which the corresponding unit livestreatment: A binary variable that signals whether the subject lived in a district where the tax was implementedpre_tax: The weekly sugar-added drink consumption in ounces before the tax was imposedpost_tax: The weekly sugar-added drink consumption in ounces after the tax was imposed
Are these wide or long format data?
soda_tax_df %>% head(10)## # A tibble: 10 × 5
## id district treatment pre_tax post_tax
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 Snake Lounge 0 1688. 1706.
## 2 2 Snake Lounge 0 427. 438.
## 3 3 Snake Lounge 0 566. 560.
## 4 4 Snake Lounge 0 607. 624.
## 5 5 Snake Lounge 0 573. 607.
## 6 6 Snake Lounge 0 496. 502.
## 7 7 Snake Lounge 0 659. 670.
## 8 8 Snake Lounge 0 498. 522.
## 9 9 Snake Lounge 0 815. 846.
## 10 10 Snake Lounge 0 503. 510.Our soda_tax_df is in wide format. We can convert our data to a long format to render the time and treatment dummy variables and save is to the soda_tax_df_long.
We will utilize the pivot_longer() function from tidyr to format our data frame.
soda_tax_df_long <-
soda_tax_df %>% # the wide format df
tidyr::pivot_longer(cols = c(pre_tax, post_tax), # both contain information about soda drank at two points in time
names_to = "period", # grab the names of pre and post and save them to period
values_to = "soda_drank") %>% # grab values from pre and post and put them in soda_drank
dplyr::mutate(after_tax = ifelse(period == "post_tax", 1, 0)) # create dummy for period
head(soda_tax_df_long, 10)## # A tibble: 10 × 6
## id district treatment period soda_drank after_tax
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 Snake Lounge 0 pre_tax 1688. 0
## 2 1 Snake Lounge 0 post_tax 1706. 1
## 3 2 Snake Lounge 0 pre_tax 427. 0
## 4 2 Snake Lounge 0 post_tax 438. 1
## 5 3 Snake Lounge 0 pre_tax 566. 0
## 6 3 Snake Lounge 0 post_tax 560. 1
## 7 4 Snake Lounge 0 pre_tax 607. 0
## 8 4 Snake Lounge 0 post_tax 624. 1
## 9 5 Snake Lounge 0 pre_tax 573. 0
## 10 5 Snake Lounge 0 post_tax 607. 1Exploring our data
We can use our soda_tax_df to explore the distribution of soda consumption at different points in time.
Let’s try first to look at the differences in the distribution only at the pre-tax time period:
ggplot(soda_tax_df, aes(x = pre_tax, fill = factor(treatment))) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.5) + # density plot with transparency (alpha = 0.5)
scale_fill_manual(name = " ", # changes to fill dimension
values = c("#a7a8aa", "#cc0055"),
labels = c("Control", "Treatment")) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
labs(title = "Distribution of soda consumption before the tax was imposed",
x = "Soda consumtion (oz)",
y = "Density")
Let’s look at the post-tax period:
ggplot(soda_tax_df, aes(x = post_tax, fill = factor(treatment))) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.5) + # density plot with transparency (alpha = 0.5)
scale_fill_manual(name = " ", # changes to fill dimension
values = c("#a7a8aa", "#cc0055"),
labels = c("Control", "Treatment")) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
labs(title = "Distribution of soda consumption after the tax was imposed",
x = "Soda consumtion (oz)",
y = "Density")
Since in our soda_tax_df_long we represent the time and soda consumption dimensions under the same columns, we can create even more complex graphs.
Let’s leverage a new layer of our grammar of graphs: Facets
We will use facet_grid() which forms a matrix of panels defined by row and column faceting variables. It is most useful when you have two discrete variables, and all combinations of the variables exist in the data.
soda_tax_df_long %>%
dplyr::mutate(period = ifelse(period == "post_tax", "T1 - Post-tax", "T0 - Pre-tax"), # create more meaningful labels
treatment = ifelse(treatment == 1, "Treated (D=1)", "Untreated (D=0)")) %>%
dplyr::group_by(period, treatment) %>% # group to extract means of each group at each time
dplyr::mutate(group_mean = mean(soda_drank)) %>% # extract means of each group at each time
ggplot(., aes(x = soda_drank, fill = factor(treatment))) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_fill_manual(name = " ", # changes to fill dimension
values = c("#cc0055", "#a7a8aa"),
labels = c("Treatment", "Control")) +
facet_grid(treatment~period) + # we specify the matrix (treatment and period)
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = group_mean), linetype = "longdash") + # add vertical line with the mean
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(x = "Soda consumed (oz)",
y = "Density")
Modeling and estimating
So far we have ignored time in our estimations. Up until this point, most of the tools we have learned produce estimates of the counterfactual through explicit assignment rules that work randomly or as-if-randomly (e.g. randomized experimental, regression discontinuity, and instrumental variable set-ups).
Difference-in-differences compares the changes in outcomes over time between units under different treatment states. This allows us to correct for any differences between the treatment and comparison groups that are constant over time assuming that the trends in time are parallel.
a. Calculating without time
If we did not have the pre_tax baseline measure, we would likely utilize the post_tax to explore the average effect on the treated. In this case, we would model this as:
after_model <- lm(post_tax ~ treatment, data = soda_tax_df)
modelsummary::modelsummary(after_model,
statistic = "conf.int",
gof_omit="AIC|BIC|Log.Lik.")| Model 1 | |
|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 523.273 |
| [518.008, 528.537] | |
| treatment | -146.918 |
| [-154.363, -139.472] | |
| Num.Obs. | 7500 |
| R2 | 0.166 |
| R2 Adj. | 0.166 |
| F | 1496.245 |
We could read this result substantively as: those who lived in districts were the tax was implemented consumed on average 146.9 ounces less of sugar-added drinks per week compared to those who lived in districts were the tax was not put in place. This calculation would give us a comparison of the treatment and control groups after treatment.
To believe the results of our after_model, we would need to believe that the mean ignorability of treatment assignment assumption is fulfilled. We would have to think carefully about possible factors that could differentiate our treatment and control groups. We use a treatment indicator based on the districts where the measure was able to be implemented. Treatment was not fully randomly assigned, so there may be lots of potential confounders that create baseline differences in the scores for those living in Old Eagleton compared to those in Snake Lounge, which also affect the after-treatment comparisons.
If we think about the mechanics behind this naive calculation, we are just comparing the average observed outcomes for those treated and not treated after the tax was imposed:
| Treatment | Average after tax |
|---|---|
| 0 | 523.27 |
| 1 | 376.35 |
ggplot(soda_tax_df, aes(x = post_tax, fill = factor(treatment))) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_fill_manual(name = " ", # changes to fill dimension
values = c("#a7a8aa", "#cc0055"),
labels = c("Control", "Treatment")) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 523.27, linetype = "longdash", color = "#a7a8aa") + #avg for the untreated
geom_vline(xintercept = 376.35, linetype = "longdash", color = "#cc0055") + #avg for the treated
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
labs(title = "Distribution of soda consumption after the tax was imposed",
x = "Soda consumtion (oz)",
y = "Density")
b. Including the time dimension (Manual extraction of the DiD estimate)
During the lecture component of the class, we learned that the \(\beta_{DD}\) is the difference in the differences. You can see it illustrated in the table. We can extract the observed values at each iteration of the treatment and time matrix and then manually subtract the differences.

| Treatment | Pre-tax | Post-tax | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 511.13 | 376.35 | -134.78 |
| 0 | 508.31 | 523.27 | 14.97 |
## [1] -149.74## [1] -149.75We can just manually subtract.
\[\beta_{DD} = -134.79 - 14.97 = -149.76\]
c. Including the time dimension (First differences on treatment indicator)
We can introduce the time component to our calculation by incorporating the pre-treatment levels of sugar-added drink consumption, which gives us the diff-in-diff estimate. We could calculate this in a fairly straightforward manner by creating a variable assessing the change in our wide format data frame:
change: The difference in sugar-added drink consumption between post- and pre-tax
soda_tax_df <- soda_tax_df %>%
dplyr::mutate(change = post_tax - pre_tax) #simple subtraction
did_model <- lm(change ~ treatment, data = soda_tax_df)
modelsummary::modelsummary(did_model,
statistic = "conf.int",
gof_omit="AIC|BIC|Log.Lik.") | Model 1 | |
|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 14.967 |
| [14.625, 15.308] | |
| treatment | -149.744 |
| [-150.228, -149.261] | |
| Num.Obs. | 7500 |
| R2 | 0.980 |
| R2 Adj. | 0.980 |
| F | 369242.378 |
We could read this result substantively as: those who lived in districts were the tax was implemented consumed on average 149.7 ounces less of sugar-added drinks per week compared to those who lived in districts were the tax was not put in place. This calculation would give us the change, or difference, in sugar-added drink consumption for treatment and control groups.
To believe the results of our did_model, we would need to believe that there are parallel trends between the two groups.
Note: when simulating the data the post_tax was defined as: \(post\_tax = 15 + pre\_tax - 150(treatment) + error\)
d. Including the time dimension (Regression formulation of the DiD model)
Remember the formula from the lecture where we estimate the diff-in-diff effect with time and treatment dummies? We can re-format our data to gather our diff-in-diff estimate.
\[Y_{it} = β_0 + β_1D^*_i + β_2P_t + β_{DD}D^∗_i × P_t + q_{it} \]
where \(D^*_i\) tell us if subject \(i\) is in the treatment group and \(P_t\) indicates the point in time (1 for post)
For this calculation we need our data in long format to use the time and treatment dummy variables.
We can see that under our long format, we have two entries for every individual. We have our variable after_tax, which represents \(P_t\), where 0 and 1 are pre- and post-tax periods respectively. We can now render our regression based on the formula:
\[Y_{it} = β_0 + β_1D^*_i + β_2P_t + β_{DD}D^∗_i × P_t + q_{it}\]
did_long_clustered_se <- estimatr::lm_robust(soda_drank ~ treatment + after_tax + treatment*after_tax,
clusters = district,
se_type = "stata",
data = soda_tax_df_long)
modelsummary::modelsummary(list(did_long_clustered_se),
statistic = "conf.int")| Model 1 | |
|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 508.306 |
| [508.077, 508.535] | |
| treatment | 2.827 |
| [-1.827, 7.480] | |
| after_tax | 14.967 |
| [14.890, 15.043] | |
| treatment × after_tax | -149.744 |
| [-150.049, -149.440] | |
| Num.Obs. | 15000 |
| R2 | 0.117 |
| R2 Adj. | 0.117 |
| se_type | stata |
If we apply the switch logic to the results, we would get the same values from the table and plots
| Treatment | Pre-tax | Post-tax | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 511.13 | 376.35 | -134.78 |
| 0 | 508.31 | 523.27 | 14.97 |
soda_tax_df_long %>%
dplyr::mutate(period = ifelse(period == "post_tax", "T1 - Post-tax", "T0 - Pre-tax"), # create more meaningful labels
treatment = ifelse(treatment == 1, "Treated (D=1)", "Untreated (D=0)")) %>%
dplyr::group_by(period, treatment) %>% # group to extract means of each group at each time
dplyr::mutate(group_mean = mean(soda_drank)) %>% # extract means of each group at each time
ggplot(., aes(x = soda_drank, fill = factor(treatment))) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_fill_manual(name = " ", # changes to fill dimension
values = c("#cc0055", "#a7a8aa"),
labels = c("Treatment", "Control")) +
facet_grid(treatment~period) + # we specify the matrix (treatment and period)
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = group_mean), linetype = "longdash") + # add vertical line with the mean
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(x = "Soda consumed (oz)",
y = "Density")
soda_tax_df_long %>%
dplyr::group_by(period, treatment) %>% # group to extract means of each group at each time
dplyr::mutate(group_mean = mean(soda_drank)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = after_tax, y = group_mean, color = factor(treatment))) +
geom_point() +
geom_line(aes(x = after_tax, y = group_mean)) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(0,1)) +
scale_color_manual(name = " ", # changes to color dimension
values = c("#a7a8aa", "#cc0055"),
labels = c("Control", "Treatment")) +
labs(x = "Time periods", y = "Ounces of soda drank per week", color = "Treatment group")+
theme_minimal() 
The mechanics behind DiD
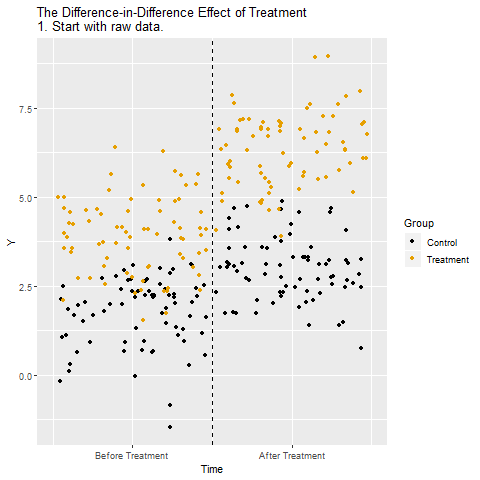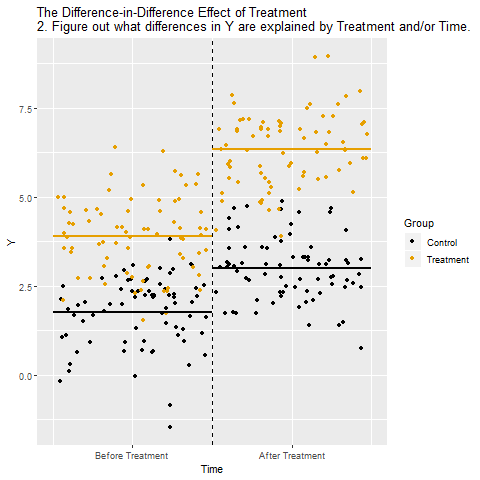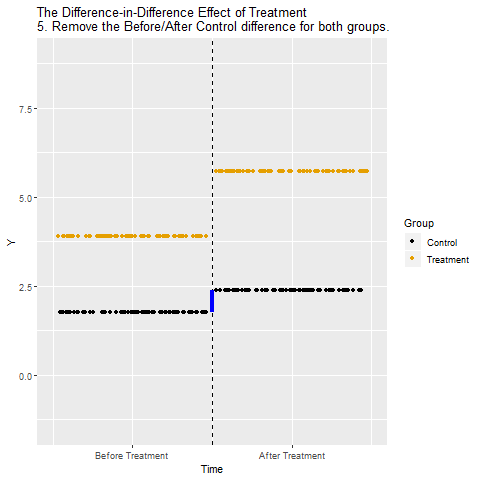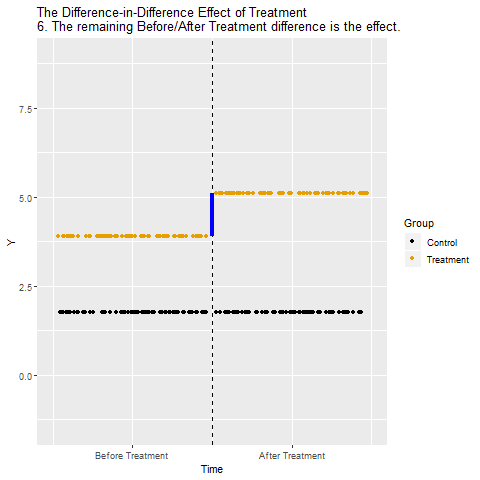
Drafting some brief recommedations
Based on your analysis of the data at hand, you decide to recommend that the tax measure should move forward in the rest of Pawnee. You state that it is a very good example of a pigouvian tax, which captures the negative externalizes not included in the market price of sugar-added drinks. The findings suggest that the tax reduced the weekly sugar-added drink consumption by about 150 liquid ounces (almost 4.5 liters).
Your evaluation report is so convincing that the Director of the Parks Department, Ron Swanson, is even doubting libertarianism.
